Why is the ocean important?

Our watery world.
But our world is a water world. The ocean covers 70% of Earth's surface. The average depth of the ocean is about 2.7 miles. In some places, the ocean is deeper than the tallest mountains are high! The ocean contains about 97% of all the water on Earth.
The ocean plays a starring role in whatever happens with the environment. One big part of its role is to soak up energy (heat) and distribute it more evenly around the Earth. Another part is to soak up CO2.
How does the ocean soak up energy?
How can a water balloon teach us about climate change? Watch this video and find out:.http://climatekids.nasa.gov/ocean/
The ocean does an excellent job of absorbing excess heat from the atmosphere. The top few meters of the ocean stores as much heat as Earth's entire atmosphere. So, as the planet warms, it's the ocean that gets most of the extra energy.
But if the ocean gets too warm, then the plants and animals that live in it must adapt—or die.

This coral has lost its algae, and thus its food source. It is sick and will probably die.
The ocean is great at sucking up CO2 from the air. It absorbs about one-quarter of the CO2 that we humans create when we burn fossil fuels (oil, coal, and natural gas.) If not for the ocean, we'd be in even worse trouble with too much CO2.
However, the ocean and everything in it are paying a price. The ocean is becoming more acidic.
What does this mean? Liquids are either acid or alkaline. Each liquid falls somewhere along a scale with acid at one end and alkaline at the other.

Normally, ocean water is less acidic than fresh
water. Unfortunately, as the ocean absorbs more and more carbon dioxide
from the atmosphere, it becomes more acidic. Lemon juice is an example
of an acidic liquid. Toothpaste is alkaline. The ocean is slightly
alkaline.
However, when the ocean absorbs a lot of CO2, the water becomes more acidic. The alkalinity of the ocean is very important in maintaining a delicate balance needed for animals to make protective shells. If the water is too acidic, the animals may not be able to make strong shells. Corals could also be affected, since their skeletons are made of the same shell-like material.
How does the ocean affect the climate?

One way the ocean affects the climate in places like Europe is by carrying heat to the north in the Atlantic Ocean. Way up north, cold water in the North Atlantic ocean sinks very deep and spreads out all around the world. The sinking water is replaced by warm water near the surface that moves to the north. Scientists call this the Great Ocean Conveyor Belt. The heat carried north helps keep the Atlantic ocean warmer in the winter time, which warms the nearby countries as well.
NASA missions that very accurately measure the hills and valleys in the ocean and changes in sea level help scientists understand what is happened with ocean currents.
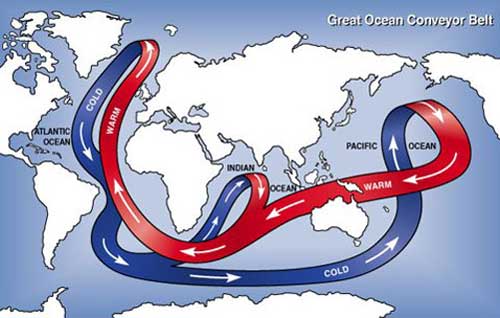 The "great ocean conveyor belt" refers to the major
ocean currents that move warm water from the equator to the poles and
cold water from the poles back toward the equator
The "great ocean conveyor belt" refers to the major
ocean currents that move warm water from the equator to the poles and
cold water from the poles back toward the equatorDoes the salt in the ocean do anything?

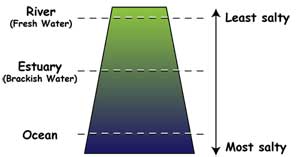
Fresh water has lower salinity (saltiness) than
estuary water, where the ocean water mixes with river water. The ocean
itself is most salty of all.
 The amount of salt in the ocean water also affects currents. Saltier
water is heavier than less salty water. When salty ocean water freezes,
the ice can no longer hold on to the salt. Instead, the salt mixes with
the water below making it saltier and heavier. Glaciers, land ice and
icebergs are made of fresh water, so what happens when this ice melts?
Good question!
The amount of salt in the ocean water also affects currents. Saltier
water is heavier than less salty water. When salty ocean water freezes,
the ice can no longer hold on to the salt. Instead, the salt mixes with
the water below making it saltier and heavier. Glaciers, land ice and
icebergs are made of fresh water, so what happens when this ice melts?
Good question!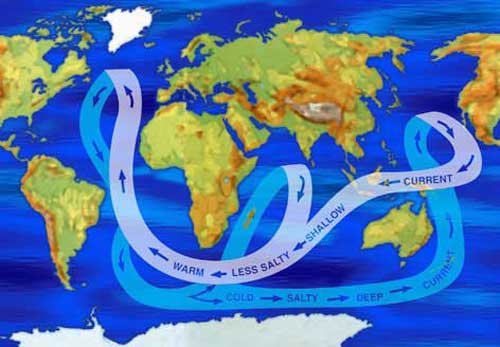
The Great Ocean Conveyor Belt carries warmer, less
salty water from the equator to the poles, and colder, saltier water
from the poles back toward the equator. Colder water and very salty
water are heavier than warmer water and less salty water.


